Hi
Guys! hope you all doing great! Today I came up with a post on an interview
question based on EMPLOYEE Table.
Task:
Update Salaries of the Employees as per below requirement.
DEPTNO
|
INCREMENT
|
10
|
100
|
20
|
200
|
30
|
300
|
40
|
400
|
X0
|
X00
|
We can notice there is a correlation
between DEPTNO and INCREMENT. For DEPTNO 10, its 100, DEPTNO 20, its 200, and
so on.......for DEPTNO X0 its X00.
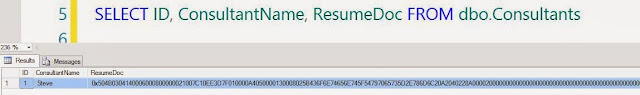
The structure of EMPLOYEE table is as below:
Input:
SELECT
EMPNO, ENAME, JOB, SAL, DEPTNO FROM EMPLOYEE;
Solution: Using WHILE Loop
DECLARE @INCREMENT INT = 100, @DEPTNO INT
DECLARE @TV TABLE (DEPTNO INT, FLAG BIT)
INSERT INTO @TV
SELECT DISTINCT DEPTNO, FLAG = 0 FROM EMPLOYEE
SET @DEPTNO = (SELECT TOP 1 DEPTNO FROM @TV WHERE FLAG = 0)
WHILE (@DEPTNO IS NOT NULL)
BEGIN
UPDATE EMPLOYEE
SET SAL = SAL + @INCREMENT
WHERE DEPTNO = @DEPTNO
UPDATE @TV
SET FLAG = 1
WHERE DEPTNO = @DEPTNO AND FLAG = 0
SET @INCREMENT = @INCREMENT + 100
SET @DEPTNO = (SELECT TOP 1 DEPTNO FROM @TV WHERE FLAG = 0)
END
Output:
SELECT
EMPNO, ENAME, JOB, SAL, DEPTNO FROM EMPLOYEE;
Conclusion: Compare both the screen shots and note that, the salaries are updated as per the requirement table mentioned on the top of this post. Hope this helps! Happy TSQL'ing ;)